Making the Case for Health Information Exchanges
I attended the OpenHIE Academy Live Event last week and learned about the function and application of the OpenHIE Architecture framework and its components. What's a health information exchange, and what does it mean for people in everyday terms?
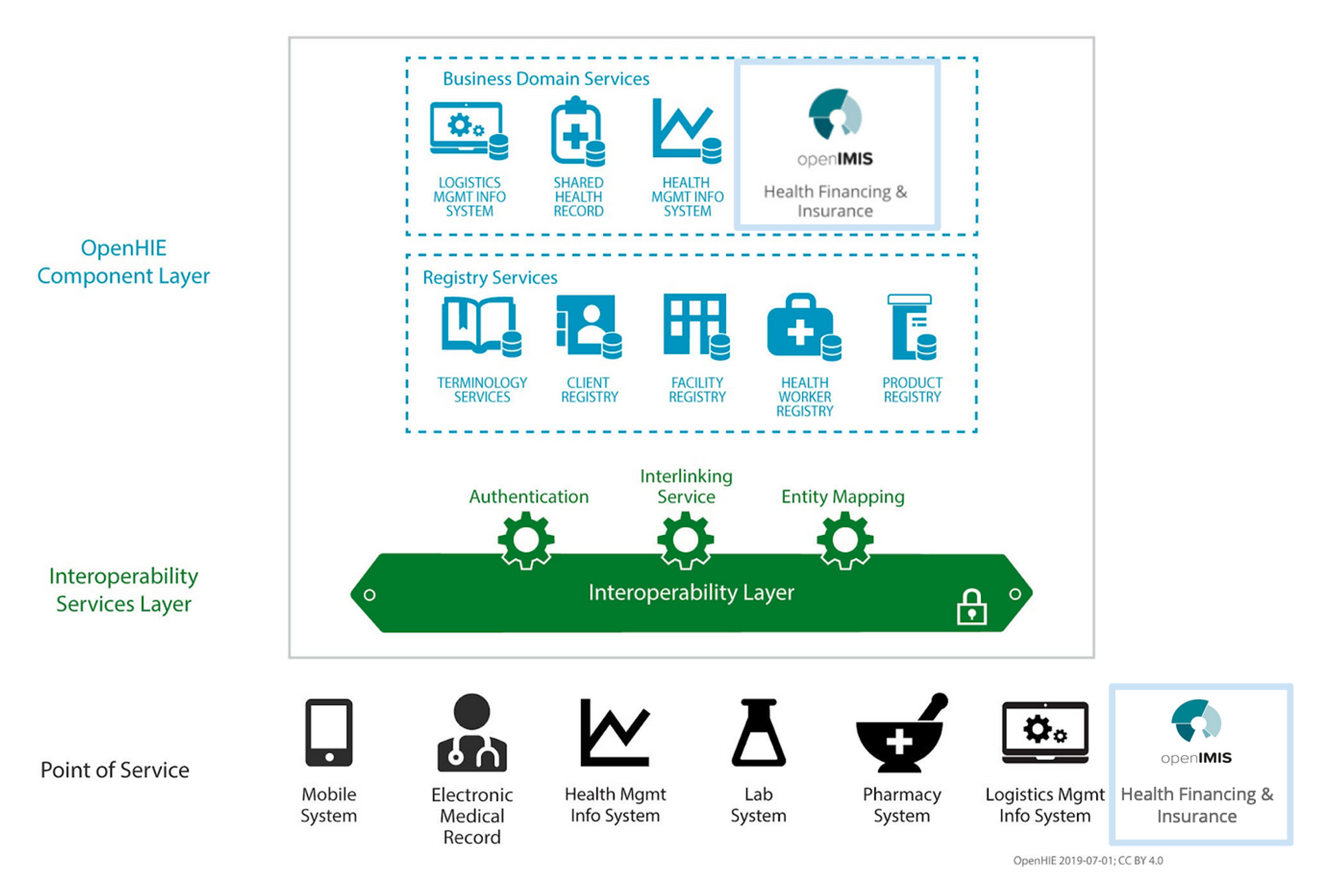
A health information exchange allows for health data to be entered once and reused across different systems by defining standards and communication protocols that enable many systems to work with the same data.
We can imagine various real world use cases for implementing a health information exchange architecture. My cousin Mariam’s experience with healthcare in Conakry serves as an example. After visiting three clinics and hospitals in Conakry, Mariam was diagnosed with kidney stones at the fourth one. All of the data that was collected in the first three clinics were not accessible to her doctor at the fourth one. At each clinic the same data was collected and doctors relied on Mariam to provide her medical history. They asked about past visits, previous diagnoses, prescriptions, lab results, etc. Her medical history was spread across paper and electronic systems, in her home, at different pharmacies, and in labs. Imagine how much faster she could have been diagnosed and treated if her healthcare workers had access to a comprehensive view of her medical history.
A health information exchange would mitigate these issues and allow data to be stored in a single database. All authorized stakeholders would be able to access and update this single health record and Mariam wouldn’t need to stress about her paper prescription she lost from years ago. Patient data is only one piece of the puzzle and other important health data such as information on facilities, providers, and supplies can also be managed in the health information exchange system.
OpenFn's Role
Two key components of a health information exchange are interoperability and data standards. The OpenFn Integration Toolkit is a tool for interoperability solution design, implementation, and adherence to data standards in health information exchange–key for organizations seeking to securely increase interoperability across systems and partners, reduce costs, strengthen health systems, and improve service delivery. Released this year, the Toolkit is a digital global good that helps health and humanitarian organizations and governments automate key processes and integrate critical information systems. It was developed in partnership with 45+ social sector partners, incorporating resources and learnings from dozens of implementations to deliver a suite of open-source documentation, implementation tools, and a templates library that fast-tracks interoperability and automation projects.
For more information visit the links below:
— Aicha
Written by
Aissatou Diallo